

Due to the arrangement of the bonds in molecules that have V-shaped, trigonal pyramidal, seesaw, T-shaped, and square pyramidal geometries, the bond dipole moments cannot cancel one another. Consequently, the bond dipole moments cannot cancel one another, and the molecule has a dipole moment. Although a molecule like CHCl 3 is best described as tetrahedral, the atoms bonded to carbon are not identical. In molecular geometries that are highly symmetrical (most notably tetrahedral and square planar, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral), individual bond dipole moments completely cancel, and there is no net dipole moment. Other examples of molecules with polar bonds are shown in Figure 2.2.9. Hence the vector sum is not zero, and H2O has a net dipole moment. (b) In H2O, the O–H bond dipoles are also equal in magnitude, but they are oriented at 104.5° to each other. Their vector sum is zero, so CO2 therefore has no net dipole. (a) In CO2, the C–O bond dipoles are equal in magnitude but oriented in opposite directions (at 180°). This charge polarization allows H 2O to hydrogen-bond to other polarized or charged species, including other water molecules.įigure 8 How Individual Bond Dipole Moments Are Added Together to Give an Overall Molecular Dipole Moment for Two Triatomic Molecules with Different Structures. We expect the concentration of negative charge to be on the oxygen, the more electronegative atom, and positive charge on the two hydrogens. Thus a molecule such as H 2O has a net dipole moment. In contrast, the H 2O molecule is not linear (part (b) in Figure 2.2.8) it is bent in three-dimensional space, so the dipole moments do not cancel each other. As a result, the CO 2 molecule has no net dipole moment even though it has a substantial separation of charge. Because the two C–O bond dipoles in CO 2 are equal in magnitude and oriented at 180° to each other, they cancel. Each C–O bond in CO 2 is polar, yet experiments show that the CO 2 molecule has no dipole moment. Such is the case for CO 2, a linear molecule (part (a) in Figure 2.2.8).
If the individual bond dipole moments cancel one another, there is no net dipole moment. The dipole moment of a molecule is therefore the vector sum of the dipole moments of the individual bonds in the molecule. Mathematically, dipole moments are vectors they possess both a magnitude and a direction. In more complex molecules with polar covalent bonds, the three-dimensional geometry and the compound’s symmetry determine whether there is a net dipole moment.
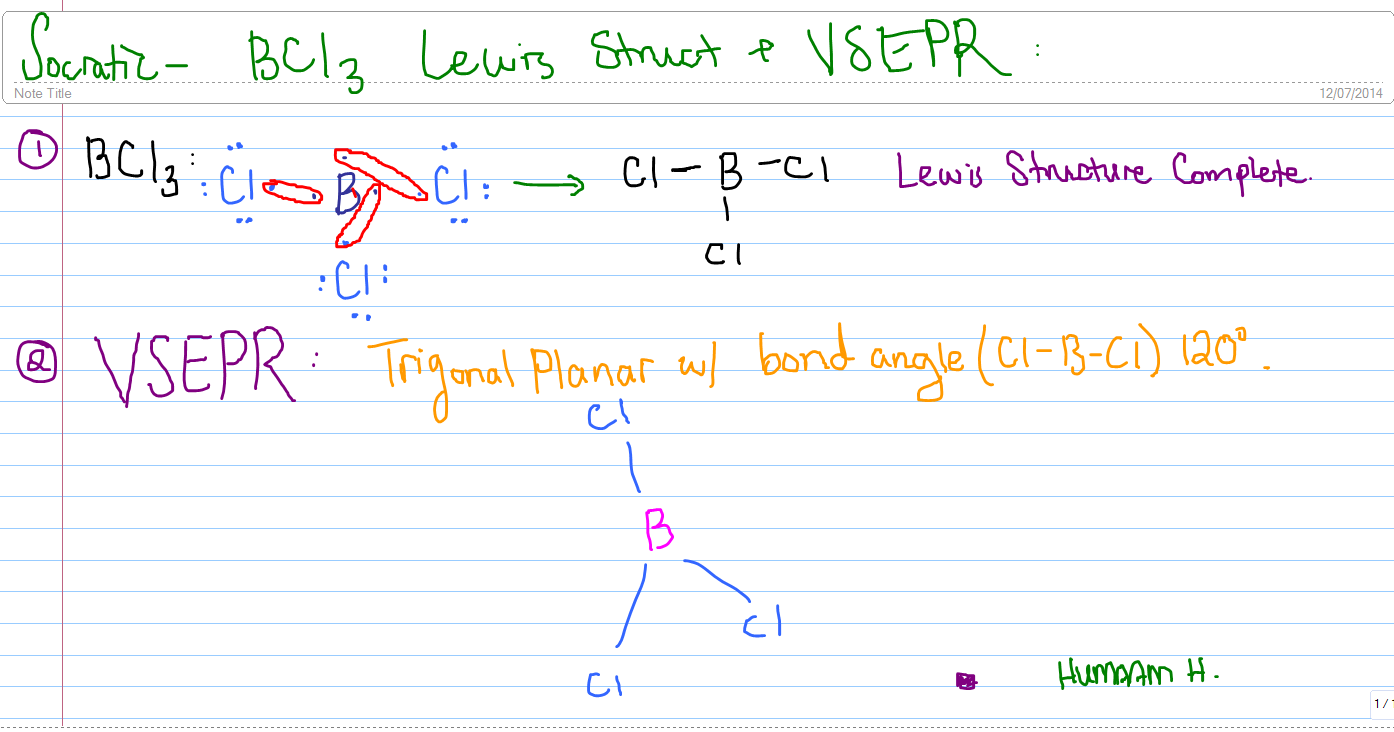
#Bcl3 dipole moment how to#
You previously learned how to calculate the dipole moments of simple diatomic molecules.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
